U.S. manufacturing stimulus expected to generate steady growth
The Inflation Reduction Act, and the CHIPs and Science Act have generated a lot of investment in manufacturing, but what is the long-term outlook for the United States?
Manufacturing insights
- Manufacturing in the United States has received a boost thanks to the Inflation Reduction Act, and the CHIPs and Science Act encouraging companies to invest in manufacturing.
- Interact Analysis projects that, in the long-term, this will generate steady growth, but the boost is nonetheless a good thing and can help change some of the old perceptions about the industry.
美国制造业无疑是经验eriencing a resurgence, helped by policies put in place by the Biden Administration, but the questions now are: “Is this a renaissance for U.S. manufacturing?” and “How long will it last?”
As the U.S. Government attempts to shore up the economy and protect it from potential geopolitical shockwaves in the future, with subsidies and incentives linked to the Inflation Reduction Act, and the CHIPs and Science Act in particular, it is undoubtedly stimulating manufacturing growth and investment in new facilities, particularly those dedicated to the production of semiconductors and electric vehicles (EVs). Recent announcements include GM and Samsung SDI unveiling plans to invest $3bn in a joint venture EV battery manufacturing plant in the US.
Furthermore, the U.S. Government incentives have also coincided with a clear trend towards reshoring and diversifying supply chains in the wake of both the COVID-19 pandemic and recent geopolitical unrest, as companies try to futureproof their operations.
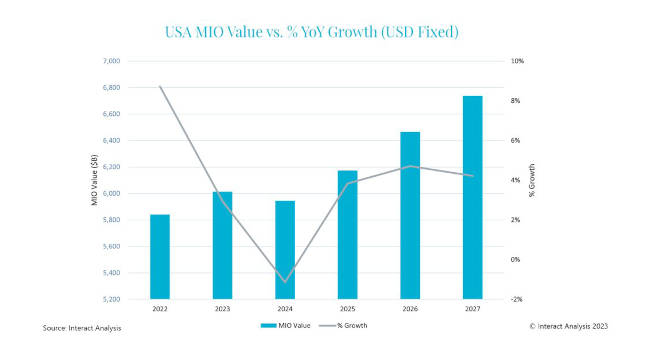
However, the impact is unlikely to be seismic, or on a New Deal scale, for a variety of reasons, including those outlined below. We are predicting year-on-year growth will remain below 10% in the medium-term with a shallow recession in 2024 and the growth rate failing to recover to 2022 levels out to 2027. Our manufacturing industry output (MIO) tracker, which quantifies the total value of manufacturing production, with deep granularity, across over 35 industries and 44 countries forecasts a good but not outstanding increase in the overall value of US manufacturing, from just over $5.8 trillion to just under $6.8 trillion during 2022 to 2027.

Interact Analysis is projecting steady, but not seismic, U.S. manufacturing growth for the future. Courtesy: Interact Analysis
First and foremost, behind expectations for a modest rather than sensational rise in U.S. production output and value are the skills and labor shortages that are already hampering US manufacturing companies, with more centrally located manufacturing companies in particular finding it hard to fill vacancies. The tight labor market means manufacturers may struggle to hire workers for new plants and we anticipate this will result in rising demand for robotics and automation technology in order achieve desired levels of productivity with reduced headcount.
其次,虽然目前的出货的数据Census Bureau is very positive and usually strongly correlates to the annual manufacturing survey (ASM), our latest forecasts anticipate a shallow recession in the US during 2024, which will constrain manufacturing growth in the short-term. Inflation rates are set to ease over time, with the US Government using interest rate hikes to reduce inflationary pressure. However, there is concern that inflation is becoming entrenched, and, if we look at the bond yields, we are now seeing an inversion larger than before any other slowdown in the last 10 years. With the possibility that short-term interest rates have exceeded what the market can reasonably bear, this is likely to spark a shallow recession. Because the consumer debt position is better than it was in the 2009 recession, the economy and manufacturing are expected to return to growth in 2025.
It also remains to be seen how Europe will respond to the U.S. manufacturing incentives, although it has clearly got Brussels rattled, with officials reportedly planning to propose sweeping reforms to rules governing state support, as well as new policies to support clean tech manufacturing and secure raw materials supply. This could set the EU and U.S. on course for a battle to attract global manufacturing investment, as the U.S. has clearly set its sights on becoming an international hub for the production of EVs and semiconductors, in particular.
Ultimately, although subsidies will attract some interest and we are forecasting growth, particularly within the target sectors, it is likely many companies will continue to manufacture where it is cheap and raw materials are plentiful, with China expected to maintain its position as the factory of the world.
–Interact Analysisis a CFE Media and Technology content partner.
Original content can be found atInteract Analysis.
Do you have experience and expertise with the topics mentioned in this content? You should consider contributing to our CFE Media editorial team and getting the recognition you and your company deserve. Clickhereto start this process.